中国における特許出願は、発明者にその発明に対する排他的権利を付与する体系的なプロセスを伴います。手続き上のステップと法的要件を理解することは、特許保護を効果的に確保するために極めて重要です。
法的枠組み
中国における特許に関する法的枠組みは、主に国内法と国際条約によって確立されている。
- 国内法:
- 中華人民共和国特許法:この法律は、中国における特許保護の基本原則と手続を概説している。
- 特許法施行規則:これらの規則は、特許法の適用と施行に関する詳細なガイドラインを規定している。
- 国際条約:
- パリ条約:加盟国間の工業所有権の保護を促進する国際協定。
- 特許協力条約(PCT):一つの国際出願で複数の国への特許出願を合理化する条約。
- ハーグ協定:この協定は、工業意匠の国際登録を認めている。
監督官庁
中国国家知識産権局(CNIPA)は、特許出願、再審査、無効審判、行政執行を担当する主要機関である。
あらゆる種類の知的財産管理に関する公式ガイドラインについてはこちらをご覧ください。
中国における特許施行
中国では、特許権の行使には行政的アプローチと司法的アプローチの両方が含まれる:
- 行政執行:中国国家知識産権局(CNIPA)と地方知識産権局は、特許侵害紛争を処理し、差止命令や侵害製品の廃棄など、迅速かつ費用対効果の高い解決策を提供している。
- 司法執行:中国各地の知的財産権専門裁判所が知的財産権侵害訴訟を審理。差し止め、損害賠償、侵害製品の廃棄などの救済措置がある。
エンフォースメントの傾向については、最新のWIPO report on patent cases in Chinaをご参照ください。
中国における特許の種類
中国は3つの主要な特許カテゴリーを認めている:
- 発明製品、プロセス、またはそれらの改良のために提案された新しい技術的スキームを意味する。
- 実用新案製品の形状や構造、またはそれらの組み合わせについて提案された、適用可能で実用的な新しい技術的スキームを意味する。
- デザイン製品の全体的または部分的な形状や模様、あるいはそれらの組み合わせ、色彩と形状や模様の組み合わせの新しいデザインを意味し、美的感覚を生み出し、産業用途に適している。についてもっと見る 中国における意匠登録の要件.
3つのタイプの違い
| アスペクト | 発明 | 実用新案 | デザイン |
|---|---|---|---|
| 保護期間 | 20年 | 10年 | 15年 |
| 審査プロセス | 実体審査、より高い特許性要件、より長い期間(1~3年) | 正式な審査、低い特許性要件、短い期間(6~12ヶ月) | 正式な試験;期間が短い(6~9カ月) |
| 主題 | プロセス、化合物、医薬品、ソフトウェアを含む技術的ソリューション(製品、方法 | テクニカル・ソリューション(製品の形状、構造) | 製品の外観(形状、色、模様) |
特許性の適格基準
新規性、進歩性、産業上の利用可能性に加え、特許出願の主題は以下のいずれにも該当してはならない:
- 科学的発見;
- 知的活動のルールと方法;
- 病気の診断・治療方法
- 動植物の品種(ただし、その生産方法は特許を取得できる);
- 核変換の方法およびそのような方法によって得られる物質;
- デザインは主に、印刷物の模様や色、あるいはそれらの組み合わせによって識別する役割を果たす。
申請ルート
- 直接申し込み:申請者は中国で直接申請できる。
- パリ・コンベンション・ルート:出願人は、他の加盟国における最初の出願から12ヶ月以内(発明または実用新案)または6ヶ月以内(意匠)に優先権を主張することができる。
- PCTルート:出願人は、特許協力条約に基づき、他の加盟国の中から中国を指定して国際出願することができます。詳細はこちら 中国の国家段階.
特許出願に必要な書類
- 発明特許:リクエストフォーム、クレーム、説明、必要な図面。
- 実用新案特許:リクエストフォーム、クレーム、説明、図面。
- デザイン特許:リクエストフォーム、画像または写真、簡単な説明。についてもっと見る 設計図面の要件.
- 委任状:代理人を通じて提出する場合。
- 優先書類優先権を主張する先の出願の認証コピーまたはDASコード。
中国における特許出願費用
かかる費用は以下の通り:
- 公式料金:出願料、審査料、助成金詳細はこちら 中国における特許料金表.
- プロフェッショナル料金:弁理士に依頼する場合
- 翻訳料金:外国語による先行出願を主張する場合。
- 年間維持費:特許の有効性を維持するため。
応募方法
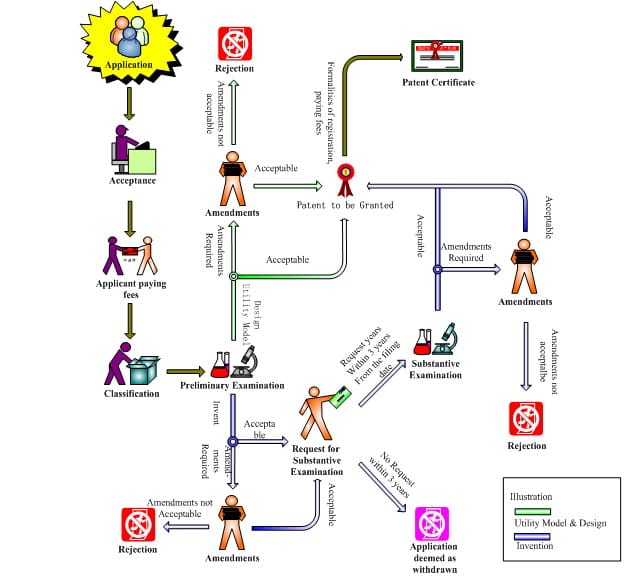
- 申請:すべての必要書類を添えてCNIPAに出願する。出願前に特許調査を行うことを強くお勧めします。
- 予備審査:CNIPAは、申請が手続き上の要件を満たしていることを確認するため、正式な審査を行う。
- 公開:発明出願の場合、最初の出願日から18ヶ月後に出願が公開される。
- 実体審査:発明出願の場合、特許性を評価するため、最初の出願日から3年以内に請求があれば実体審査が行われる。
- 付与:すべての要件が満たされると特許が付与され、特許公報に詳細が掲載されます。
申請スケジュール
- 発明特許:通常、実体審査があるため、出願から付与まで2~4年かかる。
- 実用新案・意匠特許:正式な審査のみを受けるため、通常6~12カ月で認可される。
登録特許代理人に依頼する
中国に住所または営業所を有しない外国出願人は、登録された中国特許代理人に代理を依頼しなければならない。
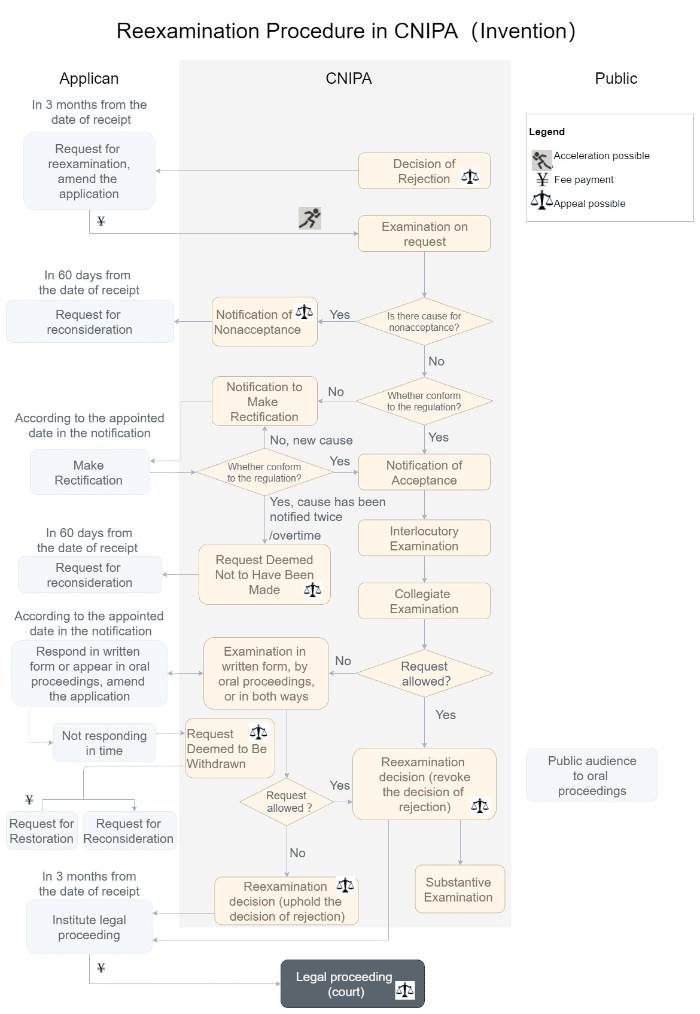
却下された申請の再審査
申請者は、CNIPAから拒絶査定を受けてから3ヶ月以内に再審査を請求することができる。
再審決定に不服がある場合、3ヶ月以内に北京知的財産権法院に上訴することができる。
補助金後のメンテナンスと執行
特許権の維持
特許付与後、特許権を維持するためには、次年度以降の年会費を支払う必要がある。この納付を怠ると、特許権が失効する可能性がある。
についてもっと見る 中国の年間料金表.
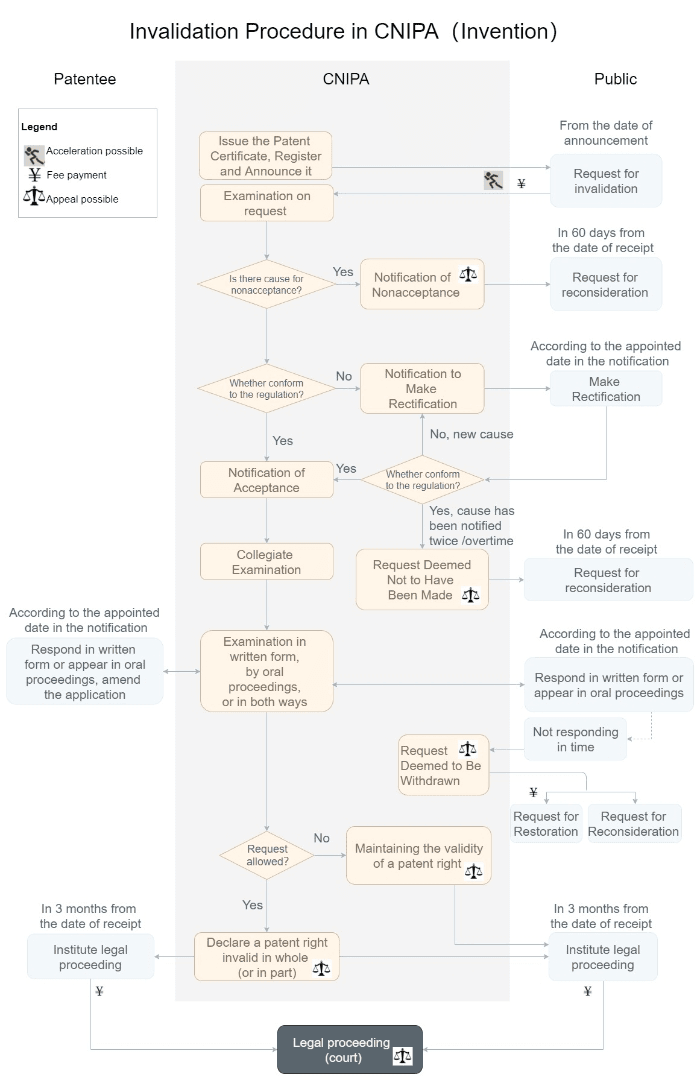
特許無効
特許が付与された後、特許が法的要件を満たしていないと判断した場合、当事者はCNIPAに対して特許の無効を請求することができる。
無効判決に不服がある場合、当事者は3ヶ月以内に北京知的財産権法院に上訴することができる。
詳細情報
続きを読む 中国における特許料金表.
続きを読む 中国における商標登録.
中国における特許の確保
中国での特許出願は、競争の激しい市場でイノベーションを保護するための重要なステップです。複雑な手続をナビゲートするには、信頼できる弁理士または法律事務所にご依頼ください。
中国特許出願に関する専門的なサポートは、今すぐ私たちのチームにご連絡ください!

